Publish Date: November 11, 2022
Researchers Led by IIT Delhi Scientist Develop a VLP-based Vaccine Candidate Against COVID-19
Share this on
New Delhi: Since the time COVID-19 pandemic started, researchers have been trying to get a better understanding of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and developing vaccines against it.
Vaccines offer a great deal of protection against the virus, but some people who have received the shots still catch COVID-19. To develop even better vaccines and treatments, ideally experiments need to be conducted with the real virus, which can only be handled in very specialized laboratories. Working with live viruses can put personnel at risk, and the requirement for specially designed settings can limit the scope of research that some teams can perform.
Instead, a safer and easier strategy is to use virus-like particles (VLPs), which are molecular mimics that look and act like a certain virus without being infectious. The particles can even serve as a vaccine themselves, as is the case with two that are currently available against the human papillomavirus.
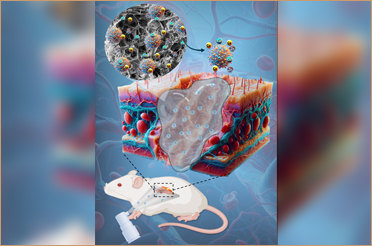
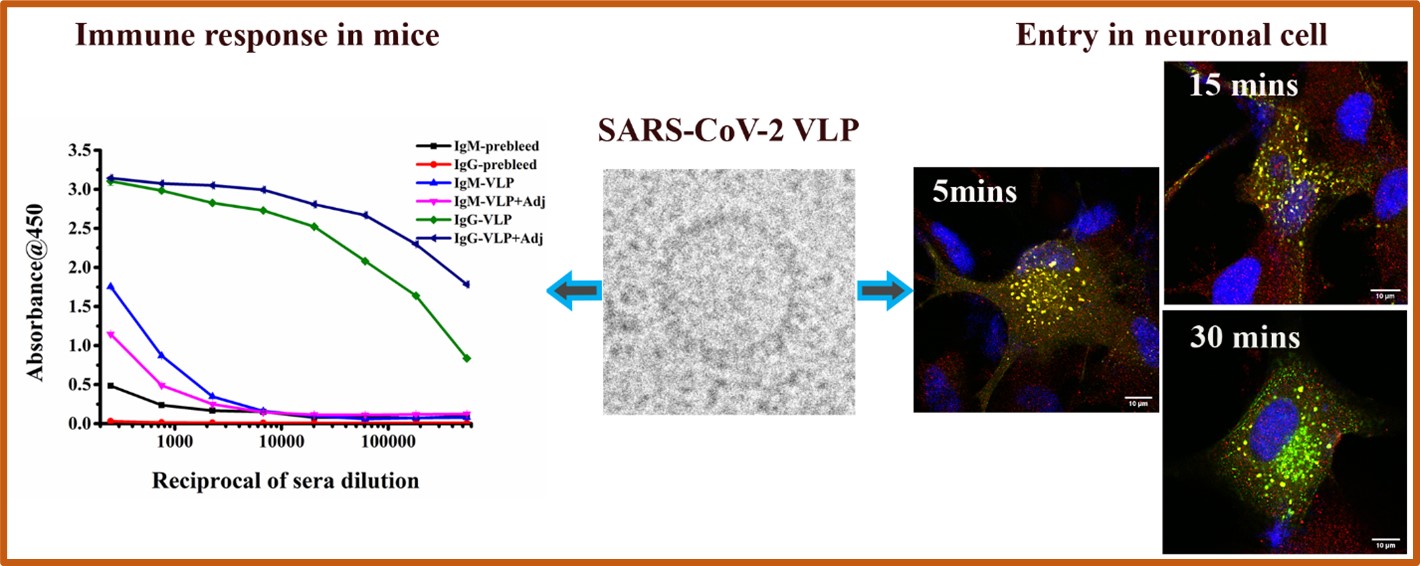
Researchers at IIT Delhi working in collaboration with the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI), Faridabad, Haryana have developed SARS-CoV-2 Virus-Like Particles (VLPs), which are a possible vaccine candidate. The VLPs tricked the immune system into launching a counterattack in mice, just as it does against SARS-CoV-2.
“The majority of the VLPs developed worldwide have utilized only the Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 as the primary antigen. However, our VLPs are as “native virus-like” as possible, which means they contain all 4 structural proteins from SARS-CoV-2 (S- Spike, N- Nucleocapsid, M- Membrane, E- Envelope). This could be an advantage in case there are several mutations in Spike in any variant, which preclude the binding of neutralizing antibodies. Animal experiments carried out at THSTI indicate that our VLPs trigger a strong adaptive immune response against multiple antigens. Vaccines based on inactivated virus naturally have this advantage, however, VLPs are safer as they are non-infectious due to lack of genome”, said Dr. Manidipa Banerjee, lead researcher and Professor in IIT Delhi’s Kusuma School of Biological Sciences.
In other experiments, the IIT Delhi researchers and their collaborators also utilized these VLPs to understand how SARS-CoV-2 could be invading cells in the Central Nervous System (CNS). COVID-19, while well-known as a respiratory illness, can also affect the nervous system, bringing on headaches and fatigue and wiping out the sense of smell, but it’s unclear whether how these symptoms are caused. The researchers showed that the VLPs could get into brain cells in petri dishes, and the process depended on both cholesterol in the cell membrane and an enzyme called dynamin.
Their study titled ‘Virus-Like Particles of SARS-CoV-2 as Virus Surrogates: Morphology, Immunogenicity, and Internalization in Neuronal Cells’ was recently published in ACS Infectious Diseases.
(Research Paper- 10.1021/acsinfecdis.2c00217)
**********